Economy of Romania: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
|poverty = 22.2% (2011 est.) |
|poverty = 22.2% (2011 est.) |
||
|gini = 33.2 (2011) |
|gini = 33.2 (2011) |
||
|edbr = |
|edbr = 73nd<ref name=" World Bank and International Financial Corporation ">{{cite web|url= http://www.doingbusiness.org/data/exploreeconomies/romania/|title= Doing Business in Romania 2013|publisher=[[World Bank]]|accessdate=2012-10-23}}</ref> |
||
|labor = 9.156 million (2012 est.) |
|labor = 9.156 million (2012 est.) |
||
|occupations = agriculture: |
|occupations = agriculture: 29%; industry: 28.6%; services: 42.4% (2010) |
||
|unemployment = {{ |
|unemployment = {{increase}}7.3% (2012 est.)<ref>[https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ro.html|publisher=[[CIA Factbook]]</ref> |
||
|average gross salary = 2,232 RON / 685 $, monthly (October 2013) |
|average gross salary = 2,232 RON / 685 $, monthly (October 2013) |
||
|industries = [[electric machinery]] and [[Electrical equipment|equipment]], textiles and footwear, light machinery and auto assembly, mining, timber, [[construction materials]], [[metallurgy]], [[chemicals]], [[food processing]], [[petroleum refining]] |
|industries = [[electric machinery]] and [[Electrical equipment|equipment]], textiles and footwear, light machinery and auto assembly, mining, timber, [[construction materials]], [[metallurgy]], [[chemicals]], [[food processing]], [[petroleum refining]] |
||
Revision as of 11:04, 16 May 2014
 | |
| Currency | Leu (Leu or RON) |
|---|---|
| Calendar year | |
Trade organisations | European Union, WTO |
| Statistics | |
| GDP | |
GDP growth | |
GDP per capita | |
GDP by sector | agriculture: 7.5%; industry: 33.0; services: 59.5% (2011 est.) |
Population below poverty line | 22.2% (2011 est.) |
| 33.2 (2011) | |
Labour force | 9.156 million (2012 est.) |
Labour force by occupation | agriculture: 29%; industry: 28.6%; services: 42.4% (2010) |
| Unemployment | |
Average gross salary | 2,232 RON / 685 $, monthly (October 2013) |
Main industries | electric machinery and equipment, textiles and footwear, light machinery and auto assembly, mining, timber, construction materials, metallurgy, chemicals, food processing, petroleum refining |
| External | |
| Exports | |
Export goods | machinery and equipment, metals and metal products, textiles and footwear, chemicals, agricultural products, minerals and fuels |
Main export partners | |
| Imports | |
Import goods | machinery and equipment, chemicals, fuels and minerals, textile and products, agricultural products |
Main import partners | |
FDI stock | |
Gross external debt | |
| Public finances | |
| Revenues | $55.67 billion (2012 est.) |
| Expenses | $59.95 billion (2012 est.) |
All values, unless otherwise stated, are in US dollars. | |
Romania has a developing, upper-middle income market economy, the 17th largest in the European Union by total nominal GDP and the 13th largest based on purchasing power parity.[7] The collapse of the Communist regime in 1989, reforms in the 2000s (decade) and its 2007 accession to the European Union have led to an improved economic outlook.
Romania has experienced growth in foreign investment with a cumulative FDI totaling more than $170 billion since 1989.[8]
Up until the late 2000s financial crisis, the Romanian economy has been referred to as a "Tiger" due to its high growth rates and rapid development.[9][10]
Until 2009, Romanian economic growth was among the fastest in Europe (officially 8.4% in 2008 and more than three times the EU average).[11][12] The country is a regional leader in multiple fields, such as IT and motor vehicle production,.[13][14][15] Bucharest, the capital city, is one of the largest financial and industrial centres in Eastern Europe.
History
Before World War II

After World War I, the application of radical agricultural reforms and the passing of a new constitution created a democratic framework and allowed for quick economic growth (industrial production doubled between 1923–1938, despite the effects of the Great Depression). With oil production of 7.2 million tons in 1937, Romania ranked second in Europe and seventh in the world.[16] The oil extracted from Romania was essential for the German war campaigns.[17]
Before World War II, Romania was Europe's second-largest food producer.[18]
Economy during 1944–1989
After the Second World War, Romania became a member of the Eastern Bloc, and switched to a socialist-style command economy. During this period the country experienced rapid industrialization in an attempt to create a "multilaterally developed socialist society". Economic growth was further fueled by foreign credits in the 1970s, but this eventually led to a growing foreign debt, which peaked at $11–12 billion.[19]
Romania's debt was largely paid off during the 1980s by implementing severe austerity measures which deprived Romanians of basic consumer goods. In 1989, before the Romanian Revolution, Romania had a GDP of about 800 billion lei, or $53.6 billion.[20] Around 58% of the country's gross national income came from industry, and another 15% came from agriculture.[20] The minimum wage was 2,000 lei, or $135.[20]
Free market transition
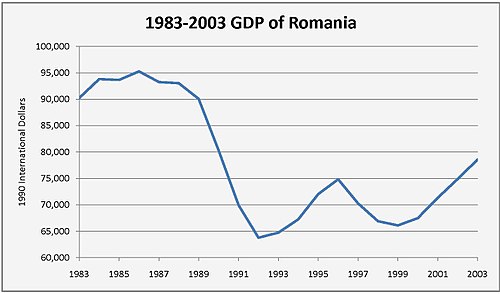
Privatization of industry was pursued with the 1992 transfer of 30% of the shares of some 6,000 state-owned enterprises to five private ownership funds, in which each adult citizen received certificates of ownership. The remaining 70% ownership of the enterprises was transferred to a state ownership fund, with a mandate to sell off its shares at the rate of at least 10% per year. The privatization law also called for direct sale of some 30 specially selected enterprises and the sale of "assets" (i.e., commercially viable component units) of larger enterprises.
As of 2008, inflation stood at 7.8%, up from 4.8% in 2007[21] estimated by the BNR at coming within 6% for the year 2006 (the year-on-year CPI, published in March 2007, is 3.66%). Also, since 2001, the economy has grown steadily at around 6–8%. Therefore, the PPP per capita GDP of Romania in 2008 was estimated to be between $12,200[22] and $14,064.[23]
Financial and technical assistance continued to flow in from the U.S., European Union, other industrial nations, and international financial institutions facilitating Romania's reintegration into the world economy. The International Monetary Fund (IMF), World Bank (IBRD), the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD), and the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) all had programs and resident representatives in Romania. Romania also attracted foreign direct investment, which in 2008 rose to $72 billion.[21]
Romania was the largest U.S. trading partner in Central-Eastern Europe until Ceauşescu's 1988 renunciation of Most Favored Nation (non-discriminatory) trading status, the latter of which resulted in high U.S. tariffs on Romanian products. Congress approved restoration of the MFN status effective 8 November 1993, as part of a new bilateral trade agreement. Tariffs on most Romanian products dropped to zero in February 1994 with the inclusion of Romania in the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP). Major Romanian exports to the U.S. include shoes and clothing, steel, and chemicals.
Romania signed an Association Agreement with the EU in 1992 and a free trade agreement with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) in 1993, codifying Romania's access to European markets and creating the basic framework for further economic integration. At the Helsinki Summit in December 1999, the European Union invited Romania to formally begin accession negotiations. In 2002, the target date of 2007 was set for Romania, along with Bulgaria, for its accession efforts. This was confirmed in 2003 at the Thessaloniki Summit and then in early 2005 Romania and Bulgaria signed the adherence treaty to EU. They formally joined the EU on 1 January 2007.
During the latter part of the Ceauşescu period, Romania earned significant credits from several Arab countries, notably Iraq, for work related to the oil industry. In August 2005, Romania agreed to forgive 43% of the US$1.7 billion debt owed by an Iraq still largely occupied by the military forces of the U.S.-led "Coalition of the Willing", making Romania the first country outside of the Paris Club of wealthy creditor nations to forgive Iraqi debts.[24]
Growth in 2000–07 was supported by exports to the EU, primarily to Italy and Germany, and a strong recovery of foreign and domestic investment. Domestic demand is playing an ever more important role in underpinning growth as interest rates drop and the availability of credit cards and mortgages increases. Current account deficits of around 2% of GDP are beginning to decline[citation needed] as demand for Romanian products in the European Union increases. Recent accession to the EU gives further impetus and direction to structural reform.
In early 2004 the government passed increases in the Value Added Tax (VAT) and tightened eligibility for social benefits with the intention to bring the public finance gap down to 4% of GDP by 2006, but more difficult pension and healthcare reforms will have to wait until after the next elections. Privatization of the state-owned bank Banca Comercială Română took place in 2005. Intensified restructuring among large enterprises, improvements in the financial sector, and effective use of available EU funds is expected to accelerate economic growth. However, the Romanian economy was affected by the Financial crisis of 2007–2008 and contracted in 2009.[25]
EU membership (2007)

- European Union member states (special territories not shown)
- 20 in the eurozone5 not in ERM II, but committed to join the eurozone on meeting the convergence criteria (Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, Romania, and Sweden)
- Non–EU member states
On 1 January 2007 Romania entered the EU. This led to some immediate international trade liberalization, but there was no shock to the economy[citation needed]. The government is running annual surpluses of above 2%.[citation needed]
This is to be contrasted with enormous current account deficits. Low interest rates guarantee availability of funds for investment and consumption. For example, a boom in the real estate market started around 2000 and has not subsided yet. At the same time annual inflation in the economy is variable and during the mid-2000s (2003–2008) has seen a low of 2.3% and high of 7.8%.
Most importantly, this poses a threat to the country's accession to the Eurozone. The Romanian government initially planned for the euro to replace the leu in 2012.[citation needed] However, experts predict that this might happen as late as in 2014.[citation needed] From a political point of view, there is a trade-off between Romania's economic growth and the stability required for early accession to the monetary union[clarification needed]. Romania's per-capita PPP GDP is still only about a 40% of the EU average, while the country's nominal GDP per capita is about 25% of the EU average.
In the winter of 2004 the government introduced a flat tax of 16% that was introduced on 1 January 2005. This is done in hope for higher GDP growth and greater tax collection rates. The reform, which some called a "revolution" in taxation, was met with mild discussions and some protests by affected working classes. Romania subsequently enjoyed the lowest fiscal burden in the European Union, until Bulgaria also switched to a flat tax of 10% in 2007.
The accession of Romania to the European Union has given the Union access to the Black Sea.
| Member State sorted by GDP |
GDP in billions of US$ (2010) |
GDP % of EU (2010) |
Annual change % of GDP (2010) |
GDP per capita in PPP US $ (2008) |
Public Debt % of GDP (2010) |
Deficit % of GDP (2010) |
Inflation % Annual (2010) |
Unemp. % (2010) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14,940 | 100.0% | 0.9 | 33,700 | 63.8 | −2.6 | 3.5 | 7.2 | |
| 262 | 2.0% | 1.5 | 14,400 | 21.2 | -4.0 | 5 | 4.4 |
2009 IMF loan
At the end of March 2009 Romania signed a deal for 20 billion Euro in loan: 12.95 Billion Euro will come from the IMF; 5 Billion Euro will come from the European Union; 1.5 Billion – from the World Bank and about 1 Billion – from other international financial institutions. The interest paid by Romania will be 3.5% per year. In return for the loan, Romanian has committed to severe cuts in public spending and wages.[27] One year later, the government cut civil servants' wages by 25%, while thousands of state jobs were axed and VAT was increased by 5% to 24%.[28]
The economy


In the Romanian press the economy has been referred to as the "Tiger of the East" during the 2000s.[10] Romania is a country of considerable economic potential: over 10 million hectares of agricultural land, diverse energy sources (coal, oil, natural gas, hydro, nuclear and wind), a substantial, if aging, manufacturing base and opportunities for expanded development in tourism on the Black Sea and in the mountains.
National budget
The national budget for 2013 was 230 billion leu (69.38 billion dollars),[29] which represents 32.9% from the GDP according to the Ministry of Finance. National budget was increasing rapidly before the financial crisis, about 8 billion dollars each year for the interval of time 2005–2009. The national defense budget was around 2.38%[30] of the GDP and was estimated at US$4.78 billion for 2008.
Economic growth
GDP growth reached 8.3% in 2006 according to the statistical office of the Romania (the year-to-year growth amounted to unexpected 9.8% in the 3rd quarter of 2006 and stayed high at 9.5% year-to-year change in the 4th quarter of 2006), and 8.0% in 2007. Table showing selected PPP GDPs and growth – 2007 to 2014 estimations, as of October 2013:[31]
| Year | GDP in billions of USD PPP |
% GDP Growth |
|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 246.750 | +6.317 |
| 2008 | 270.056 | +7.349 |
| 2009 | 254.240 | −6.576 |
| 2010 | 254.361 | −1.149 |
| 2011 | 264.953 | +2.158 |
| 2012 | 271.441 | +0.689 |
| 2013 (est.) | 280.658 | +3.5 |
| 2014 (est.) | 291.401 | +2.156 |
Romania's Gross Domestic Product at purchasing power parity (PPP) is predicted to stand at $16,982.323 per capita in 2015, when the country is expected to join[citation needed] the Eurozone. If this estimation proves correct, Romania will surpass Turkey, Bulgaria and Venezuela in this aspect.[32]
Growing middle class
Romania has growing middle and upper classes with relatively high per capita incomes. World Bank estimated that in 2002 99% of the urban and 94% of the rural population had access to electricity. In 2004, 91% of the urban and only 16% of the rural population had access to improved water supply and 94% of the urban population had access to improved sanitation.[33] In 2007 there were about 19.5 million mobile phone users in Romania[34][35] and about 7 million[36] internet users.
The net average monthly wage was 1,617 lei (€387) in March 2013.[37]The net average monthly wage was 1,192 lei (roughly 380 USD) in March 2008,[38] rose to 1,352 lei (430 USD) in 2009[39] and is expected to reach 1,819 lei (570 USD) by 2013.[40] The income from salaries in Romania had the highest growth rate in the region during 2006.[41] Despite recent growth Romania still has the lowest net average monthly wage in the European Union.[citation needed]
Currency

The leu (pronounced Template:IPA-ro), plural: lei ([ˈlej]); ISO 4217 code RON; numeric code 946) is the currency of Romania. It is subdivided into 100 bani (singular: ban). On 1 July 2005, Romania underwent a currency reform, switching from the previous leu (ROL) to a new leu (RON). 1 RON is equal to 10,000 ROL. Romania joined the European Union on 1 January 2007 and initially hoped to adopt the euro in 2014,[42] but with the deepening of the Euro crisis and with its own problems, such as a low workforce productivity, postponed its adoption plans indefinitely.[43]
The fulfillment of the Maastricht criteria
Romania, as a member state of the European Union is liable for the adoption of the common European currency, the Euro. For this reason Romania must fulfill the Maastricht criteria. Romania meets 2 out of the 5 criteria.
| Assessment month | Country | HICP inflation rate[44][nb 1] | Excessive deficit procedure[45] | Exchange rate | Long-term interest rate[46][nb 2] | Compatibility of legislation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Budget deficit to GDP[47] | Debt-to-GDP ratio[48] | ERM II member[49] | Change in rate[50][51][nb 3] | |||||
| 2012 ECB Report[nb 4] | Reference values | Max. 3.1%[nb 5] (as of 31 Mar 2012) |
None open (as of 31 Mar 2012) | Min. 2 years (as of 31 Mar 2012) |
Max. ±15%[nb 6] (for 2011) |
Max. 5.80%[nb 7] (as of 31 Mar 2012) |
Yes[52][53] (as of 31 Mar 2012) | |
| Max. 3.0% (Fiscal year 2011)[54] |
Max. 60% (Fiscal year 2011)[54] | |||||||
| 4.6% | Open | No | -0.6% | 7.25% | No | |||
| 5.2% | 33.3% | |||||||
| 2024 ECB Report[nb 8] | Reference values | Max. 3.3%[nb 9] (as of May 2024) |
None open (as of 19 June 2024) | Min. 2 years (as of 19 June 2024) |
Max. ±15%[nb 6] (for 2023) |
Max. 4.8%[nb 9] (as of May 2024) |
Yes[55][56] (as of 27 March 2024) | |
| Max. 3.0% (Fiscal year 2023)[55] |
Max. 60% (Fiscal year 2023)[55]
| |||||||
| 2025 ECB Report[nb 10] | Reference values | Max. 2.8%[nb 11] (as of April 2025) |
None open (as of 19 May 2025) | Min. 2 years (as of 19 May 2025) |
Max. ±15%[nb 6] (for 2024) |
Max. 5.1%[nb 11] (as of April 2025) |
Yes[57][58] (as of 15 April 2025) | |
| Max. 3.0% (Fiscal year 2024)[57] |
Max. 60% (Fiscal year 2024)[57] | |||||||
| 7.6% | Open | No | −0.3% | 6.4% | No | |||
| 6.6% | 48.8% | |||||||
- Notes
- ^ The rate of increase of the 12-month average HICP over the prior 12-month average must be no more than 1.5% larger than the unweighted arithmetic average of the similar HICP inflation rates in the 3 EU member states with the lowest HICP inflation. If any of these 3 states have a HICP rate significantly below the similarly averaged HICP rate for the eurozone (which according to ECB practice means more than 2% below), and if this low HICP rate has been primarily caused by exceptional circumstances (i.e. severe wage cuts or a strong recession), then such a state is not included in the calculation of the reference value and is replaced by the EU state with the fourth lowest HICP rate.
- ^ The arithmetic average of the annual yield of 10-year government bonds as of the end of the past 12 months must be no more than 2.0% larger than the unweighted arithmetic average of the bond yields in the 3 EU member states with the lowest HICP inflation. If any of these states have bond yields which are significantly larger than the similarly averaged yield for the eurozone (which according to previous ECB reports means more than 2% above) and at the same time does not have complete funding access to financial markets (which is the case for as long as a government receives bailout funds), then such a state is not to be included in the calculation of the reference value.
- ^ The change in the annual average exchange rate against the euro.
- ^ Reference values from the ECB convergence report of May 2012.[52]
- ^ Sweden, Ireland and Slovenia were the reference states.[52]
- ^ a b c The maximum allowed change in rate is ± 2.25% for Denmark.
- ^ Sweden and Slovenia were the reference states, with Ireland excluded as an outlier.[52]
- ^ Reference values from the Convergence Report of June 2024.[55]
- ^ a b Belgium, Denmark, and the Netherlands were the reference states.[55]
- ^ Reference values from the Convergence Report of June 2025.[57]
- ^ a b Finland, Ireland, and Italy were the reference states.[57]
Natural resources
Romania is an oil producer, but the current level of production isn't enough to make the country self-sufficient. Although at one time it was Europe's largest producer of oil, most of its reserves were used and squandered during the Nicolae Ceauşescu period.[citation needed] As a result, it is today a net oil and gas importer.
The pipeline network in Romania included 2,427 km for crude oil, 3,850 km for petroleum products, and 3,508 km for natural gas in 2006. Several major new pipelines are planned, especially the Nabucco Pipeline for Caspian oilfields, the longest one in the world. Romania could cash in four billion dollars from the Constanta-Trieste pipeline.[62]
Romania has considerable natural resources for a country of its size, including coal, iron ore, copper, chromium, uranium, antimony, mercury, gold, barite, borate, celestine (strontium), emery, feldspar, limestone, magnesite, marble, perlite, pumice, pyrites (sulfur), clay, arable land and hydropower.[21]
Romania's mineral production is adequate to supply its manufacturing output[citation needed]. Energy needs are also met by importing bituminous and anthracite coal and crude petroleum. In 2007 approximately 34 million tons of coal, approximately 4,000 tons of tungsten, 565,000 tons of iron ore, and 47,000 tons of zinc ore were mined. Lesser amounts of copper, lead, molybdenum, gold, silver, kaolin, and fluorite also were mined.[citation needed]
Energy

The energy sector is dominated by state-owned companies such as Termoelectrica, Hidroelectrica and Nuclearelectrica. Fossil fuels are the country's primary source of energy, followed by hydroelectric power; Romania has an estimated hydropower capacity of 36,000 GW per year.[63] Due to dependency on oil and gas imports from Russia, the country has placed an increasingly heavy emphasis on nuclear energy since the 1980s. The Cernavodă Nuclear Power Plant is currently the only one of its kind in Romania, although there are plans to build a second one in Transylvania, possibly after 2020.[64]
Wind power had an installed capacity of 76 MW in 2008,[65] and the country has the largest wind power potential in Southeast Europe, with Dobruja listed as the second best place in Europe to construct wind farms.[66] As a result, there are currently investor connection requests for over 12,000 MW.[67] There are also plans to build a number of solar power stations, such as the Covaci Solar Park, which will be one of the largest in the world.[68][69]
Of the electricity generated in 2007, 13.1 percent came from nuclear plants then in operation, 41.69 percent from thermal plants (oil and coal), and 25.8 percent from hydroelectric sites.[70]
Physical infrastructure

The volume of traffic in Romania, especially goods transportation, has increased in recent years due to its strategic location in South-East Europe. In the past few decades, much of the freight traffic shifted from rail to road. A further strong increase of traffic is expected in the future.
As of December 2012, there are only 527 km of motorways in use. At present 369 km of motorways are under construction with an estimated timetable in 2013-2016. The railway network, which was significantly expanded during the Communist years, is the fourth largest in Europe.[71]
Bucharest is the only city in Romania which as of 2009 has an underground railway system, comprising both the Bucharest Metro and the light rail system managed by Regia Autonomă de Transport Bucureşti. Although construction was planned to begin in 1941, due to geo-political factors, the Bucharest Metro was only opened in 1979. Now it is one of the most accessed systems of the Bucharest public transport network with an average ridership of 800,000 passengers during the workweek.[72] In total, the network is 67 km long and has 49 stations.[73]
Sectors of the economy
Agriculture

Agriculture employs about 29% of the population (one of the highest rates in Europe), and contributes about 8.1% of GDP. The Bărăgan is characterized by large wheat farms. Dairy products, pork, poultry, and apple production are concentrated in the western region.
Beef production is located in central Romania, while the production of fruits, vegetables, and wine ranges from central to southern Romania. Romania is a large producer of many agricultural products and is currently expanding its forestry and fishery industries. The implementation of the reforms and the Uruguay Round of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) have resulted in reforms in the agricultural sector of the economy.
Fishing
Fishing is an economic mainstay in parts of the East of Romania and along the Black Sea coast, with important fish markets in places such as Constanta and Galati. Fish such as herring, crab, lobster, haddock and cod are landed at ports such as Constanta.
There has been a large scale decrease in employment in the fishing industry within Romania due to the EU's Common Fisheries Policy, which places restrictions on the total tonnage of catch that can be landed, caused by overfishing in the Black Sea. In tandem with the decline of sea-fishing, commercial fish farms – especially in salmon, have increased in prominence in the rivers and lochs of the east of Romania. Inland waters are rich in fresh water fish such as salmon and trout.
Industry
Romania has been successful in developing its industrial sector in recent years. Industry and construction accounted for 32% of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2003, a comparatively large share even without taking into account related services. The sector employed 26.4% of the workforce. Romania excels in the production of automobiles, machine tools, and chemicals. Motor vehicle production tripled in the 2000s (decade), but still lags behind neighbouring countries such as Hungary or Ukraine.
In 2004 Romania enjoyed one of the largest world market share in machine tools (5.3%)[citation needed]. Romanian-based companies such as Dacia, Petrom, Rompetrol, Bitdefender, Romstal and Mobexpert have expanded operations throughout the region. However, small- to medium-sized manufacturing firms form the bulk of Romania's industrial sector.
Romania's industrial output is expected to advance 9% in 2007, while agriculture output is projected to grow 12%. Final consumption is also expected to increase by 11% overall – individual consumption by 14.4% and collective consumption by 10.4%. Domestic demand is expected to go up 12.7%.
Industrial output growth was 6.9% year-on-year in December 2009, making it the highest in the EU-27 zone which averaged −1.9%.[74]
Services
In 2003 service sector constituted 55% of gross domestic product (GDP), and the sector employed 51.3% of the workforce. The subcomponents of services are financial, renting, and business activities (20.5%); trade, hotels and restaurants, and transport (18%); and other service activities (21.7%). The service sector in Romania has expanded in recent years, employing some 47% of Romanians and accounting for slightly more than half of GDP.
The largest employer is the retail sector, employing almost 12% of Romanians. The retail industry is mainly concentrated in a relatively small number of chain stores clustered together in shopping malls. In recent years the rise of big-box stores, such as Cora (hypermarket) (of the France) and Carrefour (a subsidiary of the French), have led to fewer workers in this sector and a migration of retail jobs to the suburbs.
Regional variation
The strength of the Romanian economy varies from region to region. GDP, and GDP per capita is highest in Bucharest. The following table shows the GDP (2005) per capita of the 4 counties and 2 areas, with data supplied by Eurostat.[citation needed]
| Rank | Place | GDP per capita[citation needed] in dollars |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bucharest | 27,344 |
| 2 | Cluj | 26,934 |
| 3 | Timiş | 25,121 |
| 4 | Braşov | 24,788 |
| 5 | Constanţa | 24,696 |
The highest GDP per capita is found in Bucharest and surrounding Ilfov County. Values well above the national average are found in Timiş, Argeş, Braşov, Cluj, Constanţa, Sibiu and Prahova. Values well below the national average are found in: Vaslui, Botoşani, Călăraşi, Neamţ, Vrancea, Suceava, Giurgiu, Mehedinţi, Olt and Teleorman.[75]
Foreign trade

Italy is Romania's largest trading partner; two-way trade totalled some $22.6 billion in 2007. The principal exports from Italy to Romania include computers, integrated circuits, aircraft parts and other defense equipment, wheat, and automobiles, along with remittances. Romania's chief exports to Italy include cut diamonds, jewelry, integrated circuits, printing machinery, and telecommunications equipment. 2.8% of the country's GDP is derived from Agricultural activity. While Romania imports substantial quantities of grain, it is largely self-sufficient in other agricultural products and food stuffs, due to the fact that food must be regulated for sale in the Romania retail market, and hence imports almost no food products from other countries.[76]
Romania imported in 2006 food products of 2.4 billion euros, up almost 20% versus 2005, when the imports were worth slightly more than 2 billion euros. The EU is Romania's main partner in the trade with agri-food products. The exports to this destination represent 64%, and the imports from the EU countries represent 54%. Other important partners are the CEFTA countries, Turkey, Republic of Moldova and the USA.[77] Despite a decline of the arms industry in the post-communist era, Romania is a significant exporter of military equipment, accounting for 3–4% of the world total in 2007. EU members are represented by a single official at the World Trade Organization.
During the first trimester of 2010, Romanian exports increased by 21%, one of the largest rates in the European Union, surpassed only by Malta. The trade deficit currently stands at roughly 2 billion EUR, the eighth largest in the EU.[78]
Miscellaneous data
Households with access to fixed and mobile telephone access[79]
- landline telephone – 46% (2009)
- mobile telephone – 72% (2009)
Broadband penetration rate
- 13% (2010)[79]
Individuals using computer and internet[79]
- computer – 44% (2009)
- internet – 37% (2009)
See also
General:
References
- ^ "Romania Inflation Slows Further As CB Mulls End To Easing". RTT News. 12 February 2014. Retrieved 13 February 2014.
- ^ [https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ro.html%7Cpublisher=CIA Factbook
- ^ "Export Partners of Romania". CIA World Factbook. 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ^ "Import Partners of Romania". CIA World Factbook. 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ^ "Sovereigns rating list". Standard & Poor's. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ a b c Rogers, Simon; Sedghi, Ami (15 April 2011). "How Fitch, Moody's and S&P rate each country's credit rating". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 28 May 2011.
- ^ http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2009/02/weodata/groups.htm#oem
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.cambridge-news.co.uk/Universities/EUs-tiger-economy-is-tapped-by-university.htm
- ^ a b Adevarul
- ^ http://www.zf.ro/articol_172008/romania_se_indreapta_spre_o_crestere_economica_chinezeasca.html PIB-ul a crescut cu 7.5% in T1, iar anul agricol bun ar putea duce cresterea la peste 8%.
- ^ http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/main/news/10691/ The 8.2 percent growth in Romania’s economy in the first three months of 2008 was more than three times higher than the EU average
- ^ http://www.globalservicesmedia.com/Destinations/Africa-and-Middle-East/A-Glance-Inside-Bucharest,-Dubai,-Cape-Town-andGlasgow/25/23/10342/GS101221709071
- ^ Statistic definitions
- ^ http://www.ultimelestiri.com/bcr--romania-poate-adopta-euro-in-2014-23904.html
- ^ his1
- ^ http://www.adevarul.ro/actualitate/social/VIDEO_Inregistrare_senzationala_cu_Hitler-_-Fara_petrolul_din_Romania_nu_as_fi_atacat_niciodata_URSS-ul_0_379162423.html
- ^ "Business in Romania: a country that's fast off the Bloc – Two years of EU membership have transformed the business face of Romania and savvy UK firms are reaping the rewards. Paul Bray reports". The Daily Telegraph. London. 24 February 2010. Retrieved 1 May 2010.
- ^ Klepper, Nicolae. ROMANIA An Illustrated History. NY:Hippocrene Books, Inc., 2002, page 230
- ^ a b c După douăzeci de ani. Economia României în 1989, 21 decembrie 2009, standard.ro, accesat la 2 ianuarie 2010
- ^ a b c https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ro.html
- ^ GDP – per capita (PPP), The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency. Accessed on 1 October 2009
- ^ Data refer to the year 2008. PPP GDP 2008 & Population 2008, World Development Indicators database, World Bank, 15 September 2009. Note: Per capita values were obtained by dividing the PPP GDP data by the Population data.
- ^ Romania isi va recupera datoriile din Irak – BloomBiz.ro – Your Business Community
- ^ http://www.seeurope.net/?q=node/16430
- ^ http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2007/01/data/weorept.aspx?sy=2007&ey=2007&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=998&s=NGDP_RPCH%2CNGDPD%2CPPPWGT%2CPCPIPCH&grp=1&a=1&pr1.x=93&pr1.y=9
- ^ http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2009/pr09148.htm
- ^ http://www.balkaninsight.com/en/article/imf-unlocks-euro-513-m-to-romania
- ^ http://www.globaltimes.cn/content/825090.shtml#.UoXvOvlwqSo
- ^ Basescu cere 2.38% din PIB pentru armata Template:Ro
- ^ [2], IMF World Economic Outlook Database, October 2013]
- ^ International Monetary Fund, [3]
- ^ See Table 4.1
- ^ HotNews.ro – Romania are 19,5 milioane de utilizatori ai serviciilor de telefonie mobila – Arhiva noiembrie 2007
- ^ Gandul
- ^ Numarul utilizatorilor de internet din Romania a trecut de 7 milioane Template:Ro
- ^ http://www.zfenglish.com/social-politics/romania-average-net-wage-rises-4-1-in-march-10872986/ Romania Average Net Wage Rises 4.1% In March.
- ^ http://www.expres.ro/articole/detalii-articol/802680/Salariul-mediu-net-a-ajuns-la-1192-lei/ The Romanian average net wage in March 2008 is 1192 lei.
- ^ http://www.ziare.com/articole/salariu+mediu+2009
- ^ http://www.ziare.com/business/economie/03-31-2008/in-2013-salariu-mediu-net-ar-putea-ajunge-la-1-819-lei-278617
- ^ Salariul minim din Romania a avut cel mai rapid ritm de crestere din Europa Template:Ro
- ^ "Romania hopes to introduce euro in 2014". Hotnews.ro. 26 January 2007. Retrieved 14 August 2007.
- ^ Banking News (22 June 2012). "Croitoru (BNR): Adoptarea monedei euro, un orizont indepartat". Retrieved 22 July 2012.
- ^ "HICP (2005=100): Monthly data (12-month average rate of annual change)". Eurostat. 16 August 2012. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ "Excessive deficit procedures - overview". European Commission. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ "Long term government bond yields". Eurostat. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
- ^ "Government deficit/surplus, debt and associated data". Eurostat. 22 April 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- ^ "General government debt". Eurostat. Retrieved 2 June 2018.
- ^ "ERM II – the EU's Exchange Rate Mechanism". European Commission. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ "Euro/ECU exchange rates - annual data". Eurostat. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ "Former euro area national currencies vs. euro/ECU - annual data". Eurostat. Retrieved 14 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d "Convergence Report May 2012" (PDF). European Central Bank. May 2012. Retrieved 20 January 2013.
- ^ "Convergence Report - 2012" (PDF). European Commission. March 2012. Retrieved 26 September 2014.
- ^ a b "European economic forecast - spring 2012" (PDF). European Commission. 1 May 2012. Retrieved 1 September 2012.
- ^ a b c d e "Convergence Report June 2024" (PDF). European Central Bank. 26 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ "Convergence Report 2024" (PDF). European Commission. 26 June 2024. Retrieved 26 June 2024.
- ^ a b c d e "Convergence Report June 2025" (PDF). European Central Bank. 4 June 2025. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ "Convergence Report 2025" (PDF). European Commission. 4 June 2025. Retrieved 4 June 2025.
- ^ "Luxembourg Report prepared in accordance with Article 126(3) of the Treaty" (PDF). European Commission. 12 May 2010. Retrieved 18 November 2012.
- ^ "EMI Annual Report 1994" (PDF). European Monetary Institute (EMI). April 1995. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ a b "Progress towards convergence - November 1995 (report prepared in accordance with article 7 of the EMI statute)" (PDF). European Monetary Institute (EMI). November 1995. Retrieved 22 November 2012.
- ^ http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1G1-146685752.html Romania could cash in four billion dollars from the Constanta-Trieste pipeline. Pumping oil could payoff in Romania as benefits from the Constanta-Trieste pipeline could amount to more than four billion dollars. The benefits could range from 2.27 to 4.39 billion dollars over 20 years, depending on the capacity of the new oleo duct, according to Hill International's feasibility study.
- ^ Nine O'Clock, issue 4013, page 7
- ^ http://www.euractiv.ro/uniunea-europeana/articles%7CdisplayArticle/articleID_12862/Romania-contruieste-a-doua-centrala-nucleara.html
- ^ "Avalansa portugheza: Martifer pregateste o achizitie de 7 mil. euro pe eolian si un parc propriu, EDP primeste deja turbinele" (in Romanian). Business Standard. 1 April 2009. Retrieved 2 April 2009.
- ^ "Dobrogea, pe locul doi în Europa ca potenţial eolian". Dobrogea, pe locul doi în Europa ca potenţial eolian (in Romanian). Evenimentul Zilei. 5 February 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2009.
- ^ "Potential de investitii in eolian de peste 4 mld. euro". Potential de investitii in eolian de peste 4 mld. euro (in Romanian). Business Standard. 5 February 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2009.
- ^ "CJ Timis vrea sa construiasca un parc cu panouri solare, pe o suprafata de 60 de hectare" (in Romanian). Business Standard. 27 May 2009. Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ^ http://www.administratie.ro/articol.php?id=29056
- ^ Report from state power company
- ^ [4]
- ^ http://www.railway-technology.com/projects/bucharest-metro/
- ^ http://www.metrorex.ro/
- ^ http://www.financiarul.ro/2010/02/15/romania-reports-highest-december-2009-industrial-output-growth-in-eu27-2/
- ^ http://www.econtext.ro/finante-banci/bani/topul-celor-mai-bogate-judete-din-romania-dupa-pib-ul-pe-cap-de-locuitor-vezi-cati-dintre-romani-sunt-platiti-dupa-cat-muncesc.html
- ^ Romania imports agri-food products of 2.4 bn euros in 2006 – Danmarks ambassade Bukarest
- ^ Romania imports agri-food products of 2.4 bn euros in 2006 – Danmarks ambassade Bukarest
- ^ http://www.mediafax.ro/economic/romania-ocupa-locul-doi-in-ue-dupa-cresterea-exporturilor-din-primul-trimestru-6422468/
- ^ a b c IT and telecommunications in Central and Eastern Europe
