Multi Protocol File System
This article contains promotional content. (November 2012) |
The Multi Protocol File System (MPFS) is a multi-path network filesystem technology developed and sold by EMC Corporation. MPFS is intended to allow hundreds to thousands of client computer nodes to access shared computer data with higher performance than conventional NAS file sharing protocols such as NFS.
Description
MPFS technology is intended for HPC (High Performance Computing) environments. In these environments many computer nodes require concurrent access to data sets. This technology can be used to store and access data for grid computing, where the individual computing power of many systems is combined to perform a single process. Example uses include processing geological data, voice recognition datasets, and modal processing. Virtualized computing environments will also benefit from high performance shared storage.
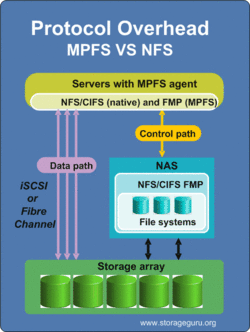
MPFS consists of an agent on the client system and a compatible NAS storage system. The client agent splits the data and meta data for the file being requested. This is done using an FMP (File Mapping Protocol) Requests for the data and its location is sent over conventional NFS to the NAS system. Data is sent and retrieved directly from the storage device via iSCSI or Fibre Channel. Retrieving the data directly from the storage device increases performance by eliminating the file system and protocol overhead associated with NFS or CIFS.
The MPFS protocol was developed by EMC for use in NAS storage environments using EMC Celerra and back end storage environments using EMC CLARiiON, EMC VNX and Symmetrix.
