Switzerland
The Swiss Confederation or Switzerland is a small landlocked federal state in central Europe, with neighbours Germany, France, Italy, Austria and Liechtenstein. The country has a strong tradition of political and military neutrality, but also of international co-operation, as it is home to many international organisations.
Confoederatio Helvetica, the Latin version of the official name, avoids choosing one of the four official languages. Its abbreviation, CH, is, for example, used as Internet TLD.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
Main article: History of Switzerland
Switzerland is a federation of relatively autonomous cantons, some of which have a history of confederacy that goes back more than 700 years, arguably putting them among the world's oldest surviving republics.
In 1291, representatives of the three forest cantons of Uri, Schwyz, and Unterwalden signed the Letter of Alliance. This united them in the struggle against "foreign" rule by the Habsburgs, who then held the German imperial throne of the Holy Roman Empire. At the Battle of Morgarten in 1315, the Swiss defeated the Habsburg army and secured quasi-independence as the Swiss Confederation.
By 1353, the three original cantons had been joined by the cantons of Glarus and Zug and the city states of Lucerne, Zürich and Berne, forming the "Old Federation" of eight states that persisted during much of the 15th century (although Zürich was expelled from the confederation during the 1440s due to a territorial conflict]]) and led to a significant increase of power and wealth of the federation, in particular due to the victories over Charles the Bold of Burgundy during the 1470s, and the success of the swiss mercenaries. The swiss victory in a war against the Suebian federation in 1499 amounted to a de facto independence from the Holy Roman Empire. The traditional order of the cantons of Switzerland reflects this state, listing the eight "Old Cantons" first, with the city states preceding the founding cantons, followed by cantons that joined the federation after 1481, in historical order.
In 1506, pope Julius II engages a Swiss Guard, that continues to serve the Vatican to the present day. The expansion of the federation, and the reputation of invincibility acquired during the earlier wars, suffered a first setback in 1515 with the swiss defeat in the Battle of Marignano.
The success of the Zwingli's reformation in some cantons led to inter-cantonal wars in 1529 and 1531 (Kappeler Kriege). The conflict between catholic and protestant cantons persisted, erupting in further violence at the battles of Villmergen in 1656 and 1712.
Under the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, European countries recognised Switzerland's independence from the Holy Roman Empire and its neutrality (ancien régime). In 1798, armies of the French Revolution conquered Switzerland. In 1803, Napoleon Bonaparte imposes a new constitution, largely restoring swiss autonomy. The Congress of Vienna of 1815 re-established Swiss independence and the European powers agreed to permanently recognise Swiss neutrality. At this time, the territory of Switzerland was increased for the last time, by the new cantons of Valais, Neuchatel and Geneva.
In 1847, a civil war broke out between the catholic and the protestant cantons (Sonderbundskrieg). Its immediate cause was a 'special treaty' (Sonderbund) of the catholic cantons. It lasted for less than a month, causing fewer than 100 casualties. Apart from small riots, this was the latest armed conflict on swiss territory.
As a consequence of the civil war, Switzerland adopted a federal constitution in 1848, amending it extensively in 1874 and establishing federal responsibility for defence, trade, and legal matters. Since then, continued political, economic, and social improvement has characterised Swiss history.
Switzerland was not involved militarily in either world war. In 1920, Switzerland joined the League of Nations, and in 1963 the Council of Europe. Women were granted the right to vote only in 1971. In 1979, parts of the canton of Berne attains independence, forming the new canton Jura.
In 2002 Switzerland finally became a full member of the United Nations.
Politics
Main article: Politics of Switzerland
Switzerland features a very unique system of government unlike any other seen in Europe, or indeed much of the world.
The bicameral Swiss parliament, the Federal Assembly, is the primary seat of power. Both houses, the Council of States and the National Council, have equal powers in all respects, including the right to introduce legislation.
Under the 1999 constitution, cantons hold all powers not specifically delegated to the federation.
The 46 members of the Council of States (two from each canton and one from former half cantons) are directly elected in each canton, whereas the 200 members of the National Council are elected directly under a system of proportional representation. Members of both houses serve for 4 years. Through referenda people may challenge any law voted by federal parliament and through initiatives introduce amendments of the federal constitution, making Switzerland a semi-direct democracy.
The top executive body and collective Head of State is the Federal Council, a collegial body of seven members. Although the constitution provides that the Assembly elects and supervises the members of the Council, the latter has gradually assumed a preeminent role in directing the legislative process as well as executing federal laws. The President of the Confederation is elected from the seven. During a one year term, he assumes special representative functions.
From 1959 to December 2003, the four major parties were represented in the Federal Council according to the "magic formula", proportional to their representation in federal parliament: 2 Christian Democrats (CVP/PDC), 2 from the Social Democrats (SPS/PSS), 2 Free Democrats (FDP/PRD), and 1 from the Swiss People's Party (SVP/UDC). This traditional distribution of seats, however, is not backed up by any law, and in the 2003 elections to the Federal Council the CVP/PDC lost their second seat to the SVP/UDC.
The function of the Federal Supreme Courts is to hear appeals of cantonal courts or the administrative rulings of the federal administration. The judges are elected by the Federal Assembly for 6-year terms.
Cantons
Main article: Cantons of Switzerland
The Swiss Confederation consists of 26 cantons:
|
[*] Cantons represented by only one councilor in the Council of States
Cantons are divided in a total of 2,889 municipalities.
Geography
Main article: Geography of Switzerland
The Swiss landscape is characterised by the Alps, a high mountain range running across the central-south of the country. Amongst the high peaks of the Swiss Alps, the highest of which is the Dufour Peak at 4,634 m, are found countless valleys, some with glaciers. From these the headwaters of several major European rivers such as the Rhine, the Rhône, the Inn, the Aare or the Ticino, flow down into lakes such as Lake Geneva, Lake Zürich, Lake Neuchâtel, and Lake Constance and farther down.

The northern, more populous part of the country is more open, but can still be fairly mountainous such as with the Jura Mountains, a smaller range in the northwest. The Swiss climate is generally temperate, but it can vary greatly locally, from the harsh conditions on the high mountains to the pleasant Mediterranean climate at Switzerland's southern tip.
See: List of lakes of Switzerland, List of rivers of Switzerland, List of mountain passes in Switzerland
Economy
Main article: Economy of Switzerland
Switzerland is a prosperous and stable modern market economy with a per capita GDP higher than that of the big western European economies. The Swiss in recent years have brought their economic practices largely into conformity with the European Union's to enhance their international competitiveness. Although the Swiss are not pursuing full EU membership, in 1999 Bern and Brussels signed agreements to further liberalise trade ties. They continue to discuss further areas for cooperation. Switzerland voted against membership in the European Economic Area in December 1992 and has since maintained and developed its relationships with other European countries via bilateral agreements.
Switzerland remains a safe haven for investors, because it has maintained a degree of bank secrecy (see Swiss bank account) and has kept up the franc's long-term external value. Swiss bank secrecy has often been controversial abroad, since, critics say, it helps criminals hide dubious transactions (corruption...) and launder money. Switzerland passed laws (such as the money laundering law of 1997) to address these concerns and does lift its bank secrecy for foreign authorities investigating crimes; However, while tax fraud (forging documents, for example) is considered a crime in Switzerland, tax evasion is not.
The GDP growth rate dipped to 1.6% in 2001, and the government projects that it will slow further to 1.3% in 2002.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Switzerland
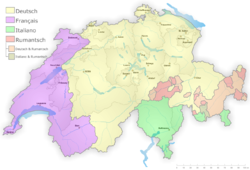
Switzerland sits at the crossroads of several major European cultures, which have heavily influenced the country's languages and cultural practices. Switzerland has four official languages: German (64%; yellow) in the north and centre, French (19%; purple) to the west, Italian (8%; green) in the south, and finally Romansh, a Romance language spoken by a small minority (<1%; red) in the southeastern canton of Graubünden. The German spoken here is predominantly a Swiss dialect known as Swiss German, but newspapers and some broadcasts use High German. Many Swiss speak more than one language and resident foreigners and temporary foreign workers make up about 20% of the population.
The largest religion in Switzerland is Roman Catholicism, to which some 43% of the population adhere. Various Protestant faiths number some 35% of the population, and immigration has established Islam (4%) and Eastern Orthodoxy (2%) as sizable minority religions. The remainder belongs to very small minorities or is unaffiliated. The stability and prosperity of Switzerland, combined with a linguistically and religiously diverse population has led some to describe the country as a consociational state.
Culture
Main article: Culture of Switzerland
The culture of Switzerland is influenced by its neighbours, but over the years a distinctive culture with strong regional differences has developed. Traditionally Switzerland is not considered one of the centres of European culture, but this conception might be deceptive.
A number of culturally active Swiss have chosen to move abroad, probably given the limited opportunities in their homeland. At the same time, the neutrality of Switzerland has attracted many creative people from all over the world. In war times the tradition of political asylum helped to attract artists, whilst recently low taxes seem predominant.
Strong regionalism in Switzerland makes it difficult to speak of a homogenous Swiss culture. The influence of German, French and Italian culture on their neighbouring parts cannot be denied. The Rhaeto-Romanic culture in the eastern mountains of Switzerland is robust.
The Swiss are noted for their banks, their chocolate, their cheese, their pocket knives, their watches, and their private boarding schools.
The tallest building in Switzerland is the Basler Messeturm.
Miscellaneous topics
- Communications in Switzerland
- Transportation in Switzerland
- Military of Switzerland
- Foreign relations of Switzerland
- Stamps and postal history of Switzerland
- Data codes for Switzerland
- List of cities in Switzerland
- List of Switzerland-related topics
- Swisstopo, topographical survey
External links
- The Federal Authorities
- The Swiss Parliament
- Federal Supreme Court - (in German, French and Italian)
- Swiss Statistics - statistics from the Swiss Federal Statistical Office
- Culturelinks.ch - a portal giving access to Swiss culture websites
- Swissworld - an encyclopedic presentation of the country by the Swiss Confederation
- About.ch - another presentation of the country
- Historical Dictionary of Switzerland - (in German, French and Italian)
- Switzerland's news and information platform - maintained by the public Swiss Broadcasting Corporation (in 9 languages)
- Spatial Planning in Switzerland Website of Swiss Federal Office for Spatial Development (land-use planning, transportation, sustainable development)