Penajam
Penajam | |
|---|---|
 Ferry port at Penajam | |
| Coordinates: 1°18′07″S 116°44′07″E / 1.301967°S 116.735195°E | |
| Country | |
| Province | East Kalimantan |
| Regency | Penajam North Paser |
| District seat | Nipah-Nipah[1] |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,207.37 km2 (466.17 sq mi) |
| Population (2023)[1] | |
• Total | 95,358 |
| • Density | 79/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 76141–76146 |
| Regional code | 64.09.01 |
| Villages | 23 |
Penajam (Indonesian pronunciation: [pəˈnadʒam]), formerly known as Balikpapan Seberang until 1987, is a district and the administrative capital of Penajam North Paser Regency, in East Kalimantan, Indonesia. As of 2023, it was inhabited by 95,358 people, and currently has the total area of 1,207.37 km2. Its district seat is located at the village of Nipah-Nipah.[1]
The district borders Sepaku to the north, Waru to the southwest, and Long Kali, Paser to the west. It is also separated from Balikpapan (of which the district formerly part of it until 1987) by the Balikpapan Bay to northeast.
History
[edit]Etymology
[edit]According to local legends, a group of robbers from this town were defeated by another group of robbers from Sangkulirang. This situation forced them to stop (Buginese: pajan) becoming robbers. This word eventually evolved into its current form, Penajam.[2]
Modern history
[edit]On 24 April 1969, Penajam was transferred from Kutai to Balikpapan by gubernatorial decree 55/TH-Pem/SK/1969.[3] Since that date, the district had been known as Balikpapan Seberang (lit. "opposite of Balikpapan") until 13 October 1987, when it was transferred again to Pasir Regency by government regulation number 21, and the name change was reverted.[4] On 11 June 1996, the northern parts of the district (12 villages) were separated to form Sepaku.[5]
On 16 October 2019, riots sparked at Penajam following an assault case at Nipah-Nipah Beach, causing damages on nearby buildings.[6]
Geography
[edit]Climate
[edit]Penajam has a tropical rainforest climate (Af) with heavy rainfall year-round.
| Climate data for Penajam | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.5 (85.1) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.0 (86.0) |
29.7 (85.5) |
29.8 (85.6) |
29.2 (84.6) |
28.6 (83.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
29.3 (84.7) |
29.9 (85.8) |
29.7 (85.5) |
29.6 (85.3) |
29.5 (85.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.1 (79.0) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.2 (79.2) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.3 (79.3) |
26.2 (79.2) |
26.3 (79.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 22.8 (73.0) |
22.9 (73.2) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.4 (74.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
23.3 (73.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
23.3 (73.9) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
23.1 (73.5) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 223 (8.8) |
191 (7.5) |
248 (9.8) |
224 (8.8) |
230 (9.1) |
195 (7.7) |
182 (7.2) |
161 (6.3) |
144 (5.7) |
140 (5.5) |
180 (7.1) |
224 (8.8) |
2,342 (92.3) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[7] | |||||||||||||
Governance
[edit]
Villages
[edit]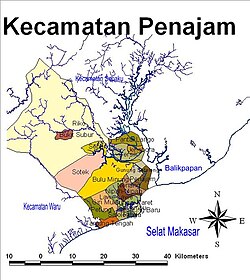

Penajam is divided into the following 23 villages (the rest are urban kelurahan, rural desa are marked by grey background):[1]
| Regional code (Kode wilayah) |
Name | Area (km2) | Population (2023) | RT (rukun tetangga) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64.09.01.1001 | Tanjung Tengah | 22.20 | 2,680 | 17 |
| 64.09.01.1002 | Salo Loang | 20.21 | 2,189 | 7 |
| 64.09.01.1003 | Petung | 10.23 | 9,981 | 11 |
| 64.09.01.1004 | Giri Mukti | 16.00 | 7,891 | 14 |
| 64.09.01.1005 | Lawe-Lawe | 60.08 | 2,911 | 18 |
| 64.09.01.1006 | Pejala | 20.45 | 1,239 | 13 |
| 64.09.01.1007 | Kampung Baru | 31.57 | 655 | 14 |
| 64.09.01.1008 | Sesumpu | 17.88 | 935 | 8 |
| 64.09.01.1009 | Sungai Parit | 19.62 | 3,745 | 8 |
| 64.09.01.1010 | Nipah-Nipah | 70.51 | 3,874 | 12 |
| 64.09.01.1011 | Nenang | 25.13 | 7,224 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1012 | Gunung Seteleng | 22.18 | 6,967 | 12 |
| 64.09.01.1013 | Penajam | 46.23 | 14,140 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1014 | Buluminung | 70.86 | 3,388 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1015 | Sotek | 157.96 | 6,475 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1016 | Sepan | 109.40 | 2,194 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1017 | Riko | 347.09 | 2,149 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1018 | Pantai Lango | 44.24 | 2,019 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.1019 | Gersik | 41.51 | 2,697 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.2020 | Jenebora | 45.02 | 3,484 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.2021 | Bukit Subur | 9.60 | 975 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.2022 | Sidorejo | 8.96 | 2,903 | 10 |
| 64.09.01.2023 | Giri Purwa | 13.47 | 4,643 | 10 |
| Totals | 1,207.37 | 95,358 | 253 |
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e "Kecamatan Penajam dalam Angka 2024". ppukab.bps.go.id. Retrieved 2024-12-27.
- ^ Mustikawati, Aquari (2019), "Jejak Budaya Penajam Paser Utara dalam Cerita Asal Usulnya", LOA, 14 (1)
- ^ Soetoen, Anwar (1979). "Pertumbuhan Pemerintahan Daerah Kabupaten Kutai dan Beberapa Faktor yang Mempengaruhinya". Dari Swapraja ke Kabupaten Kutai. Proyek Penerbitan Buku Bacaan dan Sastra Indonesia dan Daerah. p. 286–287.
- ^ "PP No. 21 Tahun 1987". peraturan.bpk.go.id. Retrieved 2024-08-23.
- ^ "PP No. 38 Tahun 1996". peraturan.bpk.go.id. Retrieved 2024-08-25.
- ^ "BNPB: 146 Rumah Terbakar Akibat Rusuh di Penajam Paser Utara". detik.com. 18 October 2019. Retrieved 29 December 2019.
- ^ "Climate: Penajam". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 24 November 2020.