Portal:Politics
| Main | Topics and categories | Tasks and projects |
The Politics portal

Politics (from Ancient Greek πολιτικά (politiká) 'affairs of the cities') is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of status or resources. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science.
Politics may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and non-violent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but the word often also carries a negative connotation. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or in a limited way, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it.
A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including warfare against adversaries. Politics is exercised on a wide range of social levels, from clans and tribes of traditional societies, through modern local governments, companies and institutions up to sovereign states, to the international level.
In modern states, people often form political parties to represent their ideas. Members of a party often agree to take the same position on many issues and agree to support the same changes to law and the same leaders. An election is usually a competition between different parties.
A political system is a framework which defines acceptable political methods within a society. The history of political thought can be traced back to early antiquity, with seminal works such as Plato's Republic, Aristotle's Politics, Confucius's political manuscripts and Chanakya's Arthashastra. (Full article...)
Selected article
The Political Cesspool is a weekly talk radio show founded by James Edwards, and syndicated by Liberty News Radio Network and Accent Radio Network. First broadcast in October 2004 twice a week from radio station WMQM, it is broadcast on Saturday nights on WLRM, a Christian radio station in Millington, Tennessee. Its sponsors include the white separatist Council of Conservative Citizens and the Institute for Historical Review, a Holocaust denial group. According to its statement of principles, the show stands for the "Dispossessed Majority" and represents "a philosophy that is pro-White." It has attracted criticism from multiple organizations for its promotion of anti-semitic, white nationalist and white supremacist views. The show features Edwards and his co-hosts Bill Rolen, Winston Smith, Keith Alexander, and Eddie Miller, as well as producer Art Frith. Its guests have included author Jerome Corsi, Minuteman Project leader Jim Gilchrist, former Constitution Party presidential candidate Michael Peroutka, actor Sonny Landham, British National Party leader Nick Griffin, Vermont secessionist Thomas Naylor, and paleoconservative activist Pat Buchanan.
Featured picture

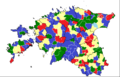
Annkathrin Kammeyer (born 1990) is a German Social Democratic politician. She became a Member of the Hamburg Parliament on 7 March 2011, the youngest person ever elected to that body.
Selected quote
Selected biography
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States from 2001 to 2009. Before that he was the 46th Governor of Texas, serving from 1995 to 2000. In a close and controversial election, Bush was elected President in 2000 as the Republican candidate, defeating Vice President Al Gore in the Electoral College. A series of terrorist attacks occurred eight months into Bush's first term as president on September 11, 2001. In response, Bush announced a global War on Terror, ordered an invasion of Afghanistan that same year and an invasion of Iraq in 2003. In addition to national security issues, Bush promoted policies on the economy, health care, education, and social security reform. Bush successfully ran for re-election against Democratic Senator John Kerry in 2004, in another relatively close election. He was a highly controversial figure internationally, with public protests occurring even during visits to close allies, such as the United Kingdom.
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that Philipp Tanzer has been an army medic, artist, firefighter, hairdresser, massage therapist, festival organiser, political candidate and gay porn star?
- ... that Ingrid Andress came up with "Lady Like" after being rejected by a man when she brought politics up?
- ... that the ideas of Albert Schädler became the founding ideas of the Progressive Citizens' Party, though he himself was opposed to the formation of political parties?
- ... that following the ban of its labour unions in 1934, the Romanian United Socialist Party would rely on its youth and women's wings for political action?
- ... that despite entering politics as part of a right-wing party, Betty Tejada was later elected president of the Chamber of Deputies as a member of the Movement for Socialism?
- ... that Jonathan Allen left journalism for politics before quitting 40 days later?
More did you know...
- ...that the first phase of Mitt Romney's 2012 U.S. presidential campaign was announced via a video message?
- ...that, at a congress in May 1921, all Socialist Party of Romania delegates who supported Bolshevik guidelines were arrested 24 hours after a vote on affiliation to the Comintern?
- ...that Ngo Dinh Diem became president of South Vietnam after a fraudulent 1955 election run by his brother Ngo Dinh Nhu, polling 133% of registered voters in Saigon?
- ...that the Brothers Grimm were amongst the Göttingen Seven, university teachers who protested changes to the constitution of the Kingdom of Hanover in 1837?
- ...that Nunez Community College in Chalmette, Louisiana, is named for the late wife of former Louisiana State Senate President Samuel B. Nunez, Jr.?
- ...that tiao-kuai is the quasi-federal administration system in China?
In this month
- June 28, 2004 - Canadian federal elections occur; the Liberal party loses its absolute majority.
News and Current events
- August 11: 4 local government areas in New South Wales, Australia locked down after COVID-19 case
- August 11: Australia: AstraZeneca vaccine access expanded by Victorian government
- August 1: Australia: Victorian lockdown lifted
- July 29: Tunisia's president dismisses prime minister, suspends parliament
- July 25: Australia: Wikinews interviews Reg Kidd, mayor of the City of Orange, about COVID-19 lockdown and local government
- July 23: South Australia enters week-long lockdown to contain COVID-19 Delta variant spread
- July 21: Technological University Dublin senior lecturer Dr Lorcan Sirr speaks to Wikinews on housing market in Ireland
- July 21: Three rural councils in New South Wales, Australia enter 7-day lockdown
- July 21: Australia: Victoria lockdown extended by a week with 85 active cases recorded
- July 15: California governor signs new state budget, eligible Californians to get stimulus payments
Topics and categories
General images
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus